Hacking group also used an IE zero-day against security researchers

An Internet Explorer zero-day vulnerability has been discovered used in recent North Korean attacks against security and vulnerability researchers.
Last month, Google disclosed that the North Korean state-sponsored hacking group known as Lazarus was conducting social engineering attacks against security researchers.
To perform their attacks, the threat actors created elaborate online ‘security researcher’ personas that would then use social media to contact well-known security researchers to collaborate on vulnerability and exploit development.

As part of this collaboration, the attackers sent malicious Visual Studio Projects and links to websites hosting exploit kits that would install backdoors on the researcher’s computers.
Microsoft also reported they had been tracking the attack and had seen Lazarus sending MHTML files to researchers containing malicious javascript. At the time of their investigation, the command and control server was down, and Microsoft could not investigate further payloads.
Internet Explorer zero-day used in attacks
Today, South Korean cybersecurity firm ENKI reported that Lazarus targeted security researchers on their team in this social engineering campaign.
While they state that the attacks failed, they analyzed the payloads downloaded by the MHT file and discovered it contained an exploit for an Internet Explorer zero-day vulnerability.
An MHT/MHTML file, otherwise known as MIME HTML, is a special file format used by Internet Explorer to store a web page and its resources in a single archive file.
The MHT file was named ‘Chrome_85_RCE_Full_Exploit_Code.mht’ and allegedly contained a Chrome 85 remote code execution exploit.
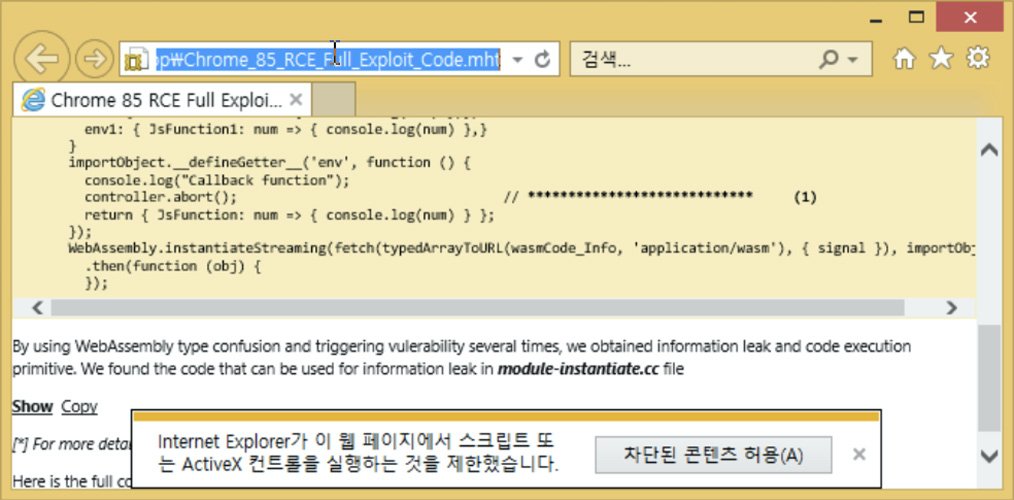
When an MHT/MHTML file is opened, Internet Explorer will automatically be used to read the file. If script execution was allowed, ENKI says that malicious javascript would download two payloads, with one containing a zero-day against Internet Explorer.
This exploit abuses a double-free bug in IE 11, allowing the attackers to upload a list of the running process, screen captures, and network information to their command and control server. It would then download and execute additional…


