TheMoon Botnet Facilitates Faceless To Exploit EoL Devices
In a digital landscape fraught with threats, vigilance is paramount. The cybercriminals are exploiting End-of-Life devices to perpetrate their malicious activities. Recently, Black Lotus Labs, the formidable threat intelligence arm of Lumen Technologies, has cast light upon a looming menace: TheMoon botnet.
This insidious entity, lurking within the shadows of outdated small office/home office (SOHO) routers and IoT devices, has resurfaced in a revamped form, bolstering a cybercriminal infrastructure known as Faceless.
TheMoon Botnet Unveiled
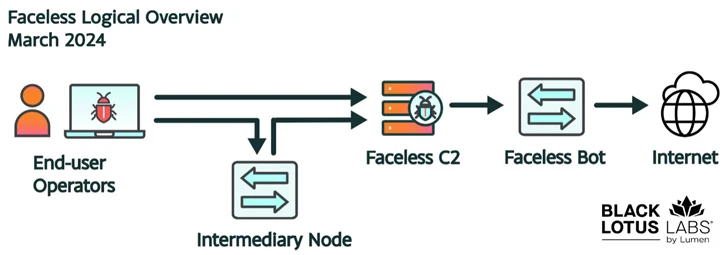
In their relentless pursuit of cyber anonymity, criminal elements have coalesced around the MoonBotnet cyber threat, leveraging its capabilities to fuel the nefarious operations of Faceless. TheMoon botnet, quietly amassing over 40,000 bots across 88 countries in a mere two months, serves as the cornerstone of this proxy service, enabling malefactors to clandestinely channel malicious traffic through compromised devices.
Mark Dehus, Senior Director of Threat Intelligence at Lumen Black Lotus Labs, underscores the gravity of the situation, elucidating how these cybercriminals exploit outdated routers to orchestrate their felonious endeavors. This symbiotic relationship between TheMoon and Faceless underscores the urgency for businesses to fortify their digital perimeters. Thus, securing home routers is essential to safeguarding personal and sensitive information from cyber threats.
Illuminating the Modus Operandi
At its core, TheMoon botnet empowers Faceless users with the cloak of anonymity, allowing them to masquerade as legitimate entities while perpetrating cyber mischief. This anonymity, devoid of any customer identification requirements, emboldens malicious actors to orchestrate TheMoon botnet attacks on vulnerable devices, siphoning valuable data with reckless abandon.
Criminal proxies powered by TheMoon botnet pose a significant threat to cybersecurity worldwide. In the face of this burgeoning threat landscape, preemptive measures become imperative. Consumers and businesses alike must adopt a proactive stance in safeguarding their digital assets. To do this, they must:
- Routinely reboot SOHO routers and promptly install…