Tag Archive for: Broke
A Single Flaw Broke Every Layer of Security in MacOS
/in Computer Security
Every time you shut down your Mac, a pop-up appears: “Are you sure you want to shut down your computer now?” Nestled under the prompt is another option most of us likely overlook: the choice to reopen the apps and windows you have open now when your machine is turned back on. Researchers have now found a way to exploit a vulnerability in this “saved state” feature—and it can be used to break the key layers of Apple’s security protections.
The vulnerability, which is susceptible to a process injection attack to break macOS security, could allow an attacker to read every file on a Mac or take control of the webcam, says Thijs Alkemade, a security researcher at Netherlands-based cybersecurity firm Computest who found the flaw. “It’s basically one vulnerability that could be applied to three different locations,” he says.
After deploying the initial attack against the saved state feature, Alkemade was able to move through other parts of the Apple ecosystem: first escaping the macOS sandbox, which is designed to limit successful hacks to one app, and then bypassing the System Integrity Protection (SIP), a key defense designed to stop authorized code from accessing sensitive files on a Mac.
Alkemade—who is presenting the work at the Black Hat conference in Las Vegas this week—first found the vulnerability in December 2020 and reported the issue to Apple through its bug bounty scheme. He was paid a “pretty nice” reward for the research, he says, although he refuses to detail how much. Since then Apple has issued two updates to fix the flaw, first in April 2021 and again in October 2021.
When asked about the flaw, Apple said it did not have any comment prior to Alkemade’s presentation. The company’s two public updates about the vulnerability are light on detail, but they say the issues could allow malicious apps to leak sensitive user information and escalate privileges for an attacker to move through a system.
Apple’s changes can also be seen in Xcode, the company’s development workspace for app creators, a blog post describing the attack from Alkemade says. The researcher says that while Apple fixed the issue for Macs running the Monterey operating system,…
Hacker says he successfully broke into security system of BPhone
/in Internet Security
By exploiting a flaw on BKAV Mobile Security, a hacker has said that he fooled the security system of BPhone to unlock the device.
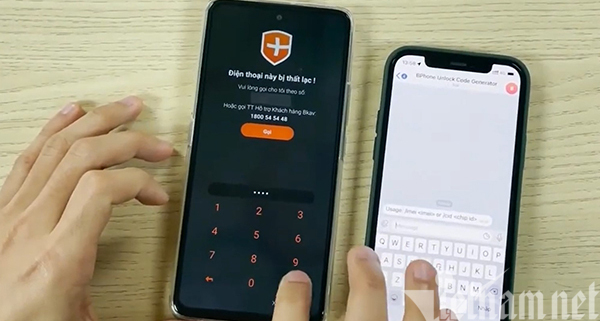
A hidden hacker recently published on his Blogspot an article on how to hack BPhone. With some technical operations, the man can crack the anti-theft feature on newly launched BPhone models.
According to the hacker, the vulnerability was discovered four years ago but it still can be exploited. To prove his finding, the hacker described in detail the flaw that he discovered.
The man discovered that the security app has the function of sending requests to BKAV’s server to check the status of the device and lock the device if necessary.
According to the hacker, BPhone communicates with a server by sending SMS messages. This is why BPhones are introduced as having anti-theft function even when there is no internet connection.
Communications are conducted every time when BPhone owners turn on the phones or change SIM. A message with encrypted information such as Chip ID, IMEI, etc will be sent to one of the telephone numbers of BKAV.
BKAV’s server, after receiving information, will check if the owners of BPhones report the loss of their devices. If the loss is confirmed, a server will send an SMS message to conduct the operation to lock the devices.
The security hole of BKAV Mobile Security occurs because it doesn’t verify the name of senders. Regardless of the sender, the system will handle messages, no matter who the senders are, if the messages follow the syntax rule.
With some technical operations, the hacker found the message structure (encrypted) that the server sends to the phone.
The hacker said he found the fixed key that BKAV uses to encrypt and decrypt data.
Thanks to finding a security hole that doesn’t verify senders, and finding the fixed key, the hacker can forge SMS messages from the server to phones to unlock devices with any passcode. This is how the hacker neutralized BPhone’s anti-theft feature.
This is the second security accident related to BKAV over the last month. In December 2021, the technology firm ran into trouble when users’ information was leaked, affecting 200 users of BKAV’s products.
BKAV’s representative, who…
Hacking group LightBasin broke into at least 13 mobile networks – report
/in Internet Security
According to a detailed report from CrowdStrike, more than a dozen mobile network operators have been infiltrated by a hacking group called LightBasin since 2019.
Importantly, the cybersecurity research firm said that the hackers were able to access subscriber information and call record details. However, the firm did not disclose the identities of the mobile network operators that were hacked, and officials did not answer questions from Light Reading about why they wouldn’t name the affected companies.
Secure mobile infrastructure “is not something that you can take for granted,” cautioned Adam Meyers, CrowdStrike’s senior VP of intelligence, in comments to Cyberscoop.
The firm’s report detailed a number of methods, both simple and complex, that the hacking group used to gain access. For example, one method involved simply attempted to log into systems using the names of standard equipment vendors.
CrowdStrike described LightBasin also known as UNC1945 as an “activity cluster” that has been targeting companies in the telecommunications sector since at least 2016. The firm said the group has some knowledge of the Chinese language but that it “does not assert a nexus between LightBasin and China.”
Another day, another attack
This isn’t the first report to call out hacks into telecom network operators. In 2019, Cybereason reported that a nation-state-backed hacking operation of Chinese origin had broken into 10 different telecom companies. However, the firm again did not name the companies that had been hacked.
“Someone was actually active in the network, going from computer to computer stealing credentials and siphoning out what can only be described as an insane amount of data hundreds of gigabytes of data,” Amit Serper, principal security researcher at Cybereason, told ZDNet at the time.
The firm said the hackers targeted companies in Europe, Africa, the Middle East and Asia, and accessed information including call data records and the geolocation of users.
But those broad reports are supplemented by more targeted hacks. For example, the US Department of Justice (DoJ) offered a detailed look at a hack into AT&T in the US….