Jet stream will get faster as climate change continues, study finds
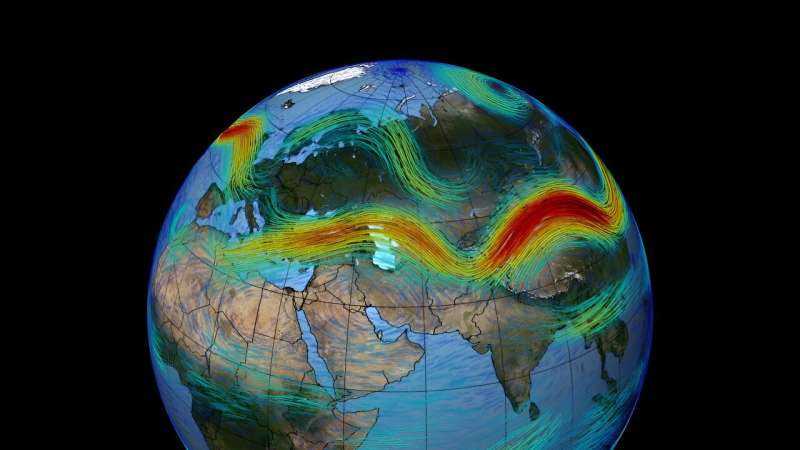
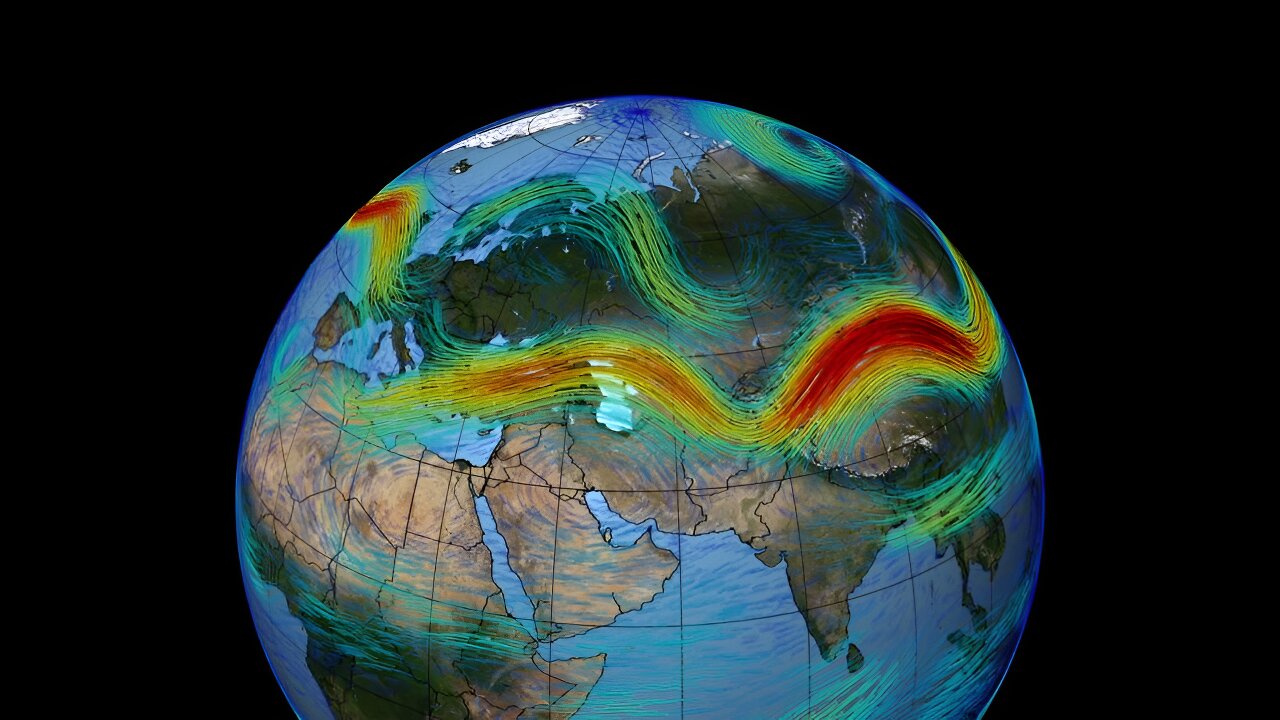
A new study in Nature Climate Change takes one of the first deep dives into how climate change will affect the fastest jet streams—the powerful, narrow winds in the upper atmosphere that steer much of the Earth’s weather systems and are connected to outbreaks of severe weather.
The research, by UChicago Prof. Tiffany Shaw and National Center for Atmospheric Research scientist Osamu Miyawaki, suggests that as the world warms, the fastest upper-level jet stream winds will get faster and faster—by about 2% for every degree Celsius the world warms. Furthermore, the fastest winds will speed up 2.5 times faster than the average wind.
“Based on these results and our current understanding, we expect record-breaking winds,” said Shaw, “and it’s likely that they will feed into decreased flight times, increased clear-air turbulence and a potential increase in severe weather occurrence.”
Wind, weather and warming
Partly prompted by recent news reports of speed-record-breaking flights over the Atlantic, Shaw and Miyawaki began to investigate and realized there had been very little exploration of how the very fastest jet stream winds would respond to climate change.
To fill this gap, they combined climate change models with what we know about the physics of jet streams.
Jet streams usually move from west to east around the globe in the upper atmosphere, about six miles (10 kilometers) above us. We know that jet streams strongly influence the weather we experience on the ground—especially air temperature, winds and weather patterns, and storms. They also influence the occurrence of severe storms, tornadoes, hail and severe wind.
Jet streams form because of the contrast between the cold, dense air at the poles and the warm, light air in the tropics, in combination with the rotation of the Earth. (This was first shown in…