Crooks manipulate GitHub’s search results to distribute malware
Crooks manipulate GitHub’s search results to distribute malware
Researchers warn threat actors are manipulating GitHub search results to target developers with persistent malware.
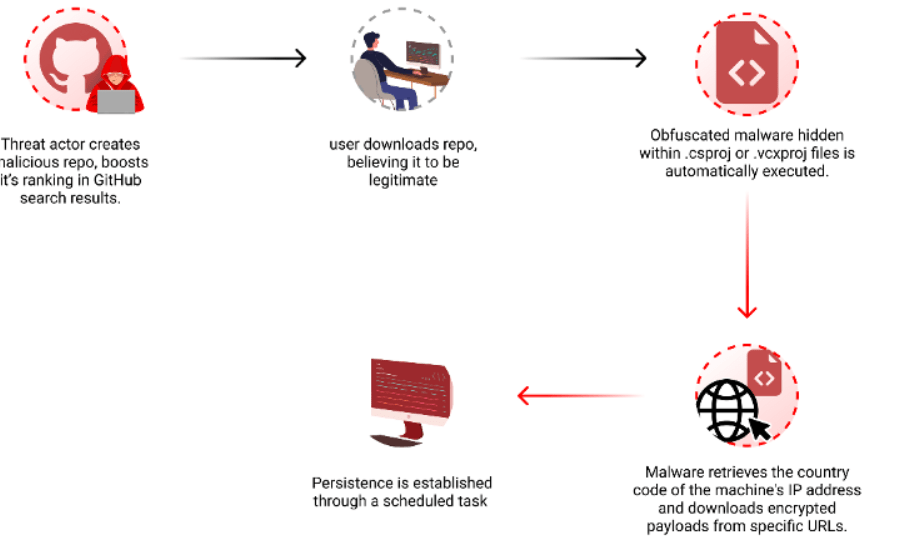
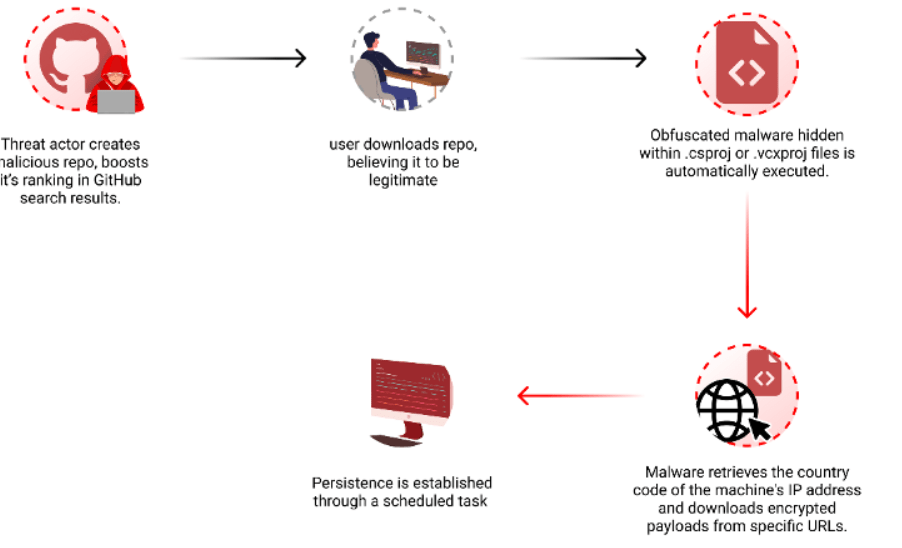
Checkmarx researchers reported that threat actors are manipulating GitHub search results to deliver persistent malware to developers systems.
Attackers behind this campaign create malicious repositories with popular names and topics, they were observed using techniques like automated updates and fake stars to boost search rankings.
“By leveraging GitHub Actions, the attackers automatically update the repositories at a very high frequency by modifying a file, usually called “log”, with the current date and time or just some random small change. This continuous activity artificially boosts the repositories’ visibility, especially for instances where users filter their results by “most recently updated,” increasing the likelihood of unsuspecting users finding and accessing them.” reads the report published by Checkmarx. “While automatic updates help, the attackers combine another technique to amplify the effectiveness of their repo making it to the top results. The attackers employed multiple fake accounts to add bogus stars, creating an illusion of popularity and trustworthiness.”
To evade detection, threat actors concealed the malicious code in Visual Studio project files (.csproj or .vcxproj), it is automatically executed when the project is built.
The researchers noticed that the payload is delivered based on the victim’s origin, and is not distributed to users in Russia.
In the recent campaign, the threat actors used a sizable, padded executable file that shares similarities with the “Keyzetsu clipper” malware.
The recent malware campaign involves a large, padded executable file that shares similarities with the “Keyzetsu clipper” malware, targeting cryptocurrency wallets.
On April 3rd, the attacker updated the code in one of their repositories, linking to a new URL that downloads a different encrypted .7z file. The archive contained an executable named feedbackAPI.exe.
Threat actors padded the executable with numerous zeros…