Rise of Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: Enterprise Software Now a Prime Target for Hackers With 64% YoY Surge
In the fast-paced world of cybersecurity, “zero-day” vulnerabilities loom as a formidable challenge for tech giants investing billions in enhancing user experiences. These vulnerabilities are mostly software flaws that developers fail to detect, leaving no immediate patches or fixes available to protect against potential exploitation. According to a recent report, “Google’s Threat Analysis Group,” the year 2023 witnessed a significant rise in the exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities.
To be precise, the exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities increased a notable 56.5% YoY, from 62 in 2022 to 97 in 2023. However, this number fell short of the record set in 2021, when 106 zero-day vulnerabilities were observed being exploited.
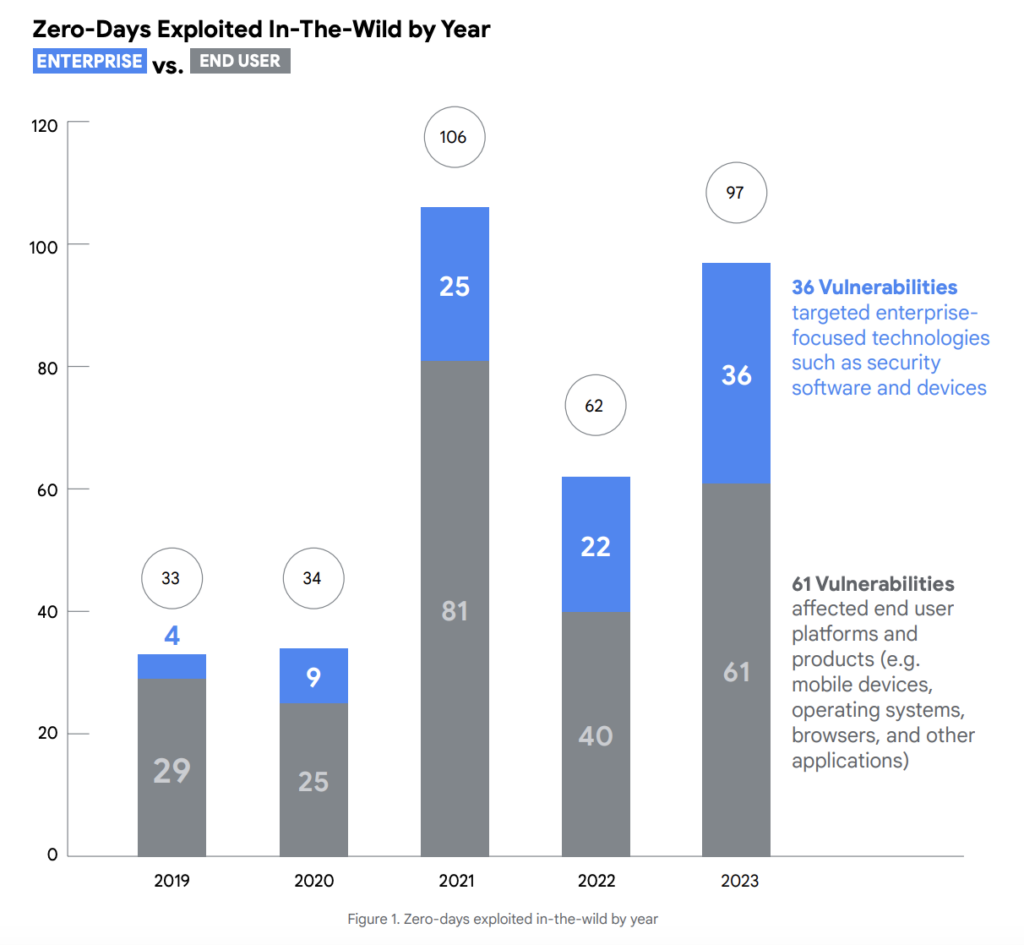

The surge in vulnerability exploitation suggests that hackers are becoming more aggressive and adept at discovering and using vulnerabilities to launch cyberattacks.
As these vulnerabilities are exploited, Commercial Surveillance Vendors (CSVs) emerge as key players in the cyber threat ecosystem. In 2023, CSVs were responsible for 75% of known zero-day exploits targeting Google products and Android ecosystem devices, comprising 13 out of 17 vulnerabilities. These CSVs specialize in selling spyware capabilities to government clients for surveillance activities.
Out of the 37 zero-day vulnerabilities exploited in browsers and mobile devices in 2023, more than 60% were attributed to Commercial Surveillance Vendors (CSVs).
Attackers have also increased their efforts to exploit vulnerabilities within third-party components and libraries. This strategy was chosen because exploiting these vulnerabilities could potentially impact multiple products simultaneously.
Threat actors across various motivations actively sought out vulnerabilities in products or components that offered broad access to multiple targets, reflecting a scalable and effective approach to launching attacks.
It is important to note that there was a whopping 64% YoY increase in the number of vulnerabilities targeted by hackers in enterprise-specific technologies during 2023. This trend was further evidenced by the widening range of enterprise vendors targeted since at least 2019,…




