Google Confirms Massive Increase In Zero-Day Vulnerabilities Exploited In Attacks Due To Spyware Vendors
Both its Threat Analysis Group, as well as the company’s subsidiary firm Mandiant, mentioned how the figures continue to grow as we speak and a lot of that has to do with spyware vendors.
The figures reached 97 zero-days and that stood for more than a 50% rise when you compare it to the past which was just 62. But despite such an increase, the numbers are still much lower than the rise of 106 seen back in the year 2021.
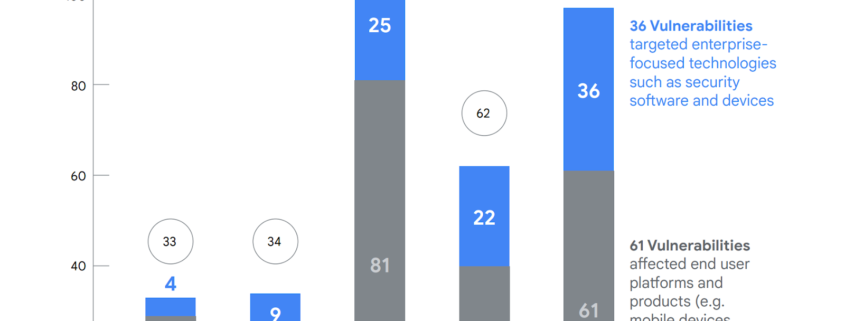
Both entities collectively witnessed 29 out of the 97 vulnerabilities. They even spoke about 61 impacted end users who made use of Google’s products and services such as mobile phones, browsers, and social media apps.
Furthermore, the rest of them were utilized to attack tech like security software and a host of other leading devices in this regard. As far as the enterprise side is concerned, there’s a mega array of vendors as well as products under target and we’re seeing more specific tech getting impacted as a result of this.
Let’s not forget how they’ve seen that as the years pass by, the faster they’re discovering the patch featuring bugs from attackers and this means shorter lifespans arising due to the exploit in question.
In 2023, plenty of threat actors made use of zero-day vulnerabilities that went up to Figure 10. And interestingly, it was China that was highlighted as being behind most of the attacks that had support from the government. Some of those entailed espionage groups from the country which was a trend moving upward.
In 2023, it was all thanks to commercial surveillance that seemed to be the culprit of these attacks that kept on targeting both Android as well as Google devices.
They include up to 75% of all those zero-day exploitations that kept on hitting the platforms. In addition to that, there were vendors
Other than that, most of the 37 zero-day vulnerabilities found on browsers as well as devices that were exploited in 2023 had Google linking close to 60% of all CSVs that keep on selling spyware to clients in the government.
Way back in February, Google revealed how so many…