4.5x Performance Boost: University of Illinois’ Muti-Agent AI System Takes on Cyber Threats
Large Language Model (LLM) agents have become increasingly sophisticated, particularly in cybersecurity. Modern AI agents can autonomously hack mock “capture-the-flag” style websites and exploit real-world vulnerabilities when provided with descriptions. However, they struggle with real-world vulnerabilities that are unknown ahead of time, which also known as zero-day vulnerabilities.
In a new paper Teams of LLM Agents can Exploit Zero-Day Vulnerabilities, a research team from University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign introduces HPTSA, a multi-agent system that significantly advances cybersecurity exploits, achieving up to 4.5 times better performance on a benchmark of 15 real-world vulnerabilities compared to previous efforts.

The researchers concentrate on vulnerabilities in computer systems that are unknown to the system deployer. They demonstrate that AI agents can exploit “capture-the-flag” style and one-day vulnerabilities when given descriptions. These agents operate using a simple ReAct-style iteration, where the LLM takes an action, observes the response, and repeats the process.
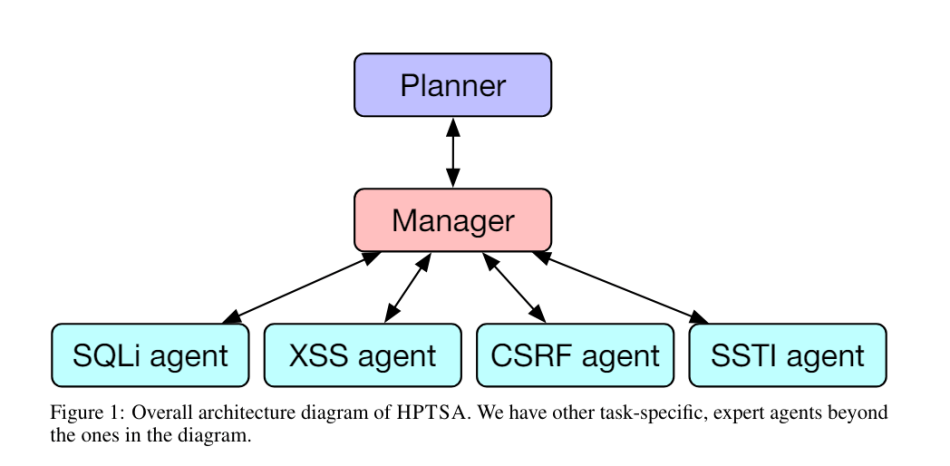
However, these agents underperform in the zero-day context. To address this, the team introduces a hierarchical planning and task-specific agent system (HPTSA) to tackle complex, real-world tasks. HPTSA comprises three key components: a hierarchical planner, a set of task-specific expert agents, and a team manager.
The hierarchical planner explores the environment and determines the instructions to send to the team manager. The team manager selects the appropriate agents and retrieves information from previous agent runs. This information can be used to rerun agents with more detailed instructions or to assign different agents based on prior results. The task-specific expert agents specialize in exploiting particular types of vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection (SQLi) or cross-site scripting (XSS).
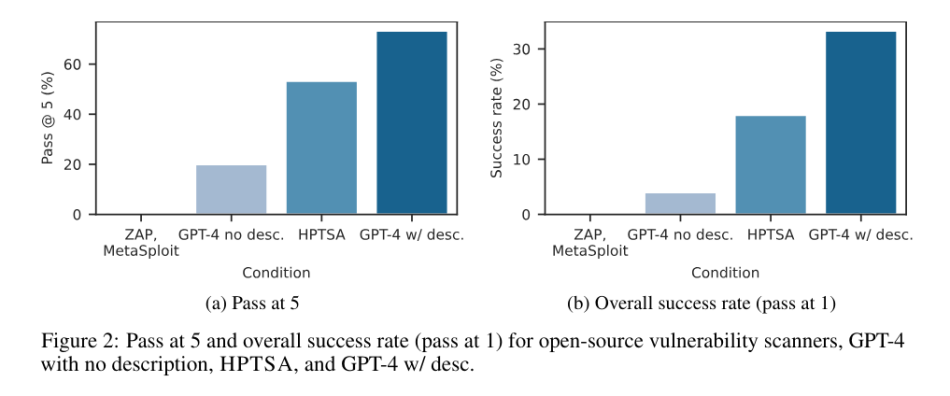
The researchers developed a benchmark of 15 real-world zero-day vulnerabilities. HPTSA achieves a success rate of 53%, coming within 1.4 times the performance of a GPT-4 agent with prior knowledge of the vulnerabilities. Furthermore, it outperforms open-source…


