Observations on Resolver Behavior During DNS Outages
When an outage affects a component of the internet infrastructure, there can often be downstream ripple effects affecting other components or services, either directly or indirectly. We would like to share our observations of this impact in the case of two recent such outages, measured at various levels of the DNS hierarchy, and discuss the resultant increase in query volume due to the behavior of recursive resolvers.
During the beginning of October 2021, the internet saw two significant outages, affecting Facebook’s services and the .club top level domain, both of which did not properly resolve for a period of time. Throughout these outages, Verisign and other DNS operators reported significant increases in query volume. We provided consistent responses throughout, with the correct delegation data pointing to the correct nameservers.
While these higher query rates do not impact Verisign’s ability to respond, they raise a broader operational question—whether the repeated nature of these queries, indicative of a lack of negative caching, might potentially be mistaken for a denial-of-service attack.
On Oct. 4, 2021, Facebook experienced a widespread outage, lasting nearly six hours. During this time most of its systems were unreachable, including those that provide Facebook’s DNS service. The outage impacted facebook.com, instagram.com, whatsapp.net and other domain names.
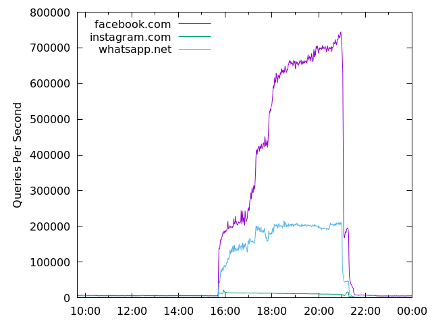
Under normal conditions, the .com and .net authoritative name servers answer about 7,000 queries per second in total for the three domain names previously mentioned. During this particular outage, however, query rates for these domain names reached upwards of 900,000 queries per second (an increase of more than 100x), as shown in Figure 1 below.
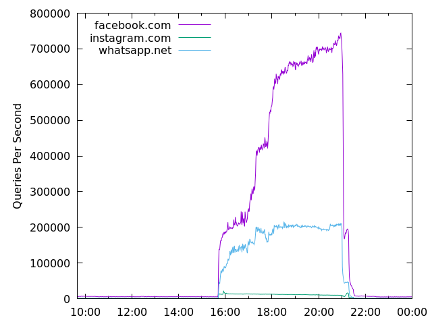
During this outage, recursive name servers received no response from Facebook’s name servers—instead, those queries timed out. In situations such as this, recursive name servers generally return a SERVFAIL or “server failure” response, presented to end users as a “this site can’t be reached” error.
Figure 1 shows an increasing query…