Tag Archive for: Do’s
Are Decade-Old DoS Tools Still Relevant in 2021?
/in Internet Security
Surprisingly, the answer is yes.
After Anonymous fell apart in 2016, the threat landscape shifted rapidly. The once mainstream group of organized Denial of Service (DoS) attacks with simple GUI-based tools were no more; as the era of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks and DDoS-as-a-Service began to take shape under the power of new IoT botnets such as Bashlite and Mirai.
While Anonymous has not entirely disappeared, its digital footprint has significantly reduced over the last five years. Today, you can still find Anonymous accounts on the usual social media outlets and video platforms spreading operational propaganda, but with limited impact compared to the past. However, during a recent Anonymous operation, I was surprised to find that the group, which still uses PasteBin and GhostBin (to centralize operational details), had updated their target list from years prior and suggested the use of Memcached and other reflective attack vectors. They recommended using antiquated DoS tools, such as LOIC, HOIC, ByteDoS, and Pyloris, all nearly 10-years-old.
Tools of The Past
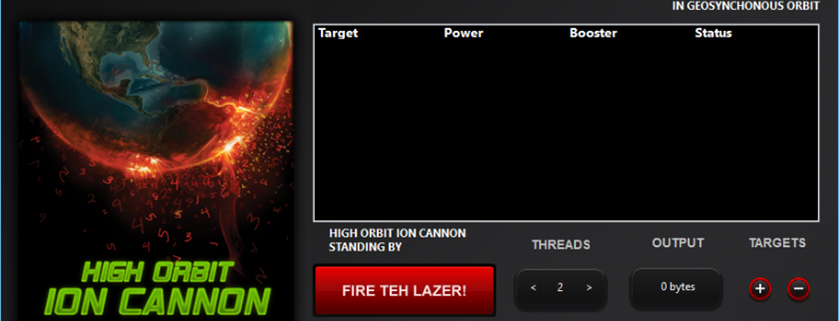
HOIC
High Orbit Ion Cannon, or HOIC for short, is a network stress testing tool related to LOIC; both are used to launch Denial of Service attacks popularized by Anonymous. This tool can cause a Denial of Service through the use of HTTP floods. Additionally, HOIC has a built-in scripting system that accepts .hoic files called boosters. These files allow a user to deploy anti-DDoS randomization countermeasures and increase the magnitude of the attack.
While it has no significant obfuscation or anonymization techniques to protect the user’s origin, the use of .hoic “booster” scripts allows the user to specify a list of rotating target URLs, referrers, user agents, and headers. This effectively causes a Denial of Service condition by attacking multiple pages on the same site while making it seem like attacks are coming from several different users.

[Click for Full Report: Quarterly Threat Intelligence Report]
ByteDOS
Once considered a destructive tool, ByteDoS has become a novelty in 2021. ByteDos is a Windows desktop DoS application. It is a simple, standalone executable file that does…