State-Sponsored Hackers Exploit Two Cisco Zero-Day Vulnerabilities for Espionage
A new malware campaign leveraged two zero-day flaws in Cisco networking gear to deliver custom malware and facilitate covert data collection on target environments.
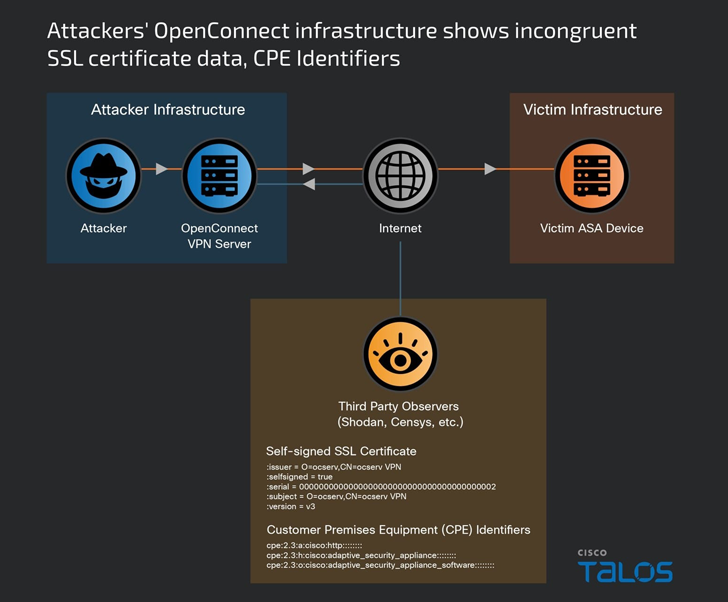
Cisco Talos, which dubbed the activity ArcaneDoor, attributed it as the handiwork of a previously undocumented sophisticated state-sponsored actor it tracks under the name UAT4356 (aka Storm-1849 by Microsoft).
“UAT4356 deployed two backdoors as components of this campaign, ‘Line Runner’ and ‘Line Dancer,’ which were used collectively to conduct malicious actions on-target, which included configuration modification, reconnaissance, network traffic capture/exfiltration and potentially lateral movement,” Talos said.
The intrusions, which were first detected and confirmed in early January 2024, entail the exploitation of two vulnerabilities –
- CVE-2024-20353 (CVSS score: 8.6) – Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance and Firepower Threat Defense Software Web Services Denial-of-Service Vulnerability
- CVE-2024-20359 (CVSS score: 6.0) – Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance and Firepower Threat Defense Software Persistent Local Code Execution Vulnerability
It’s worth noting that a zero-day exploit is the technique or attack a malicious actor deploys to leverage an unknown security vulnerability to gain access into a system.
While the second flaw allows a local attacker to execute arbitrary code with root-level privileges, administrator-level privileges are required to exploit it. Addressed alongside CVE-2024-20353 and CVE-2024-20359 is a command injection flaw in the same appliance (CVE-2024-20358, CVSS score: 6.0) that was uncovered during internal security testing.
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has added the shortcomings to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, requiring federal agencies to apply the vendor-provided fixes by May 1, 2024.
The exact initial access pathway used to breach the devices is presently unknown, although UAT4356 is said to have started preparations for it as early as July 2023.
A successful foothold is followed by the deployment of two implants named Line Dancer and Line Runner, the former of which is an…