New KV-Botnet Targeting Cisco, DrayTek, and Fortinet Devices for Stealthy Attacks
A new botnet consisting of firewalls and routers from Cisco, DrayTek, Fortinet, and NETGEAR is being used as a covert data transfer network for advanced persistent threat actors, including the China-linked threat actor called Volt Typhoon.
Dubbed KV-botnet by the Black Lotus Labs team at Lumen Technologies, the malicious network is an amalgamation of two complementary activity clusters that have been active since at least February 2022.
“The campaign infects devices at the edge of networks, a segment that has emerged as a soft spot in the defensive array of many enterprises, compounded by the shift to remote work in recent years,” the company said.
From USER to ADMIN: Learn How Hackers Gain Full Control
Discover the secret tactics hackers use to become admins, how to detect and block it before it’s too late. Register for our webinar today.
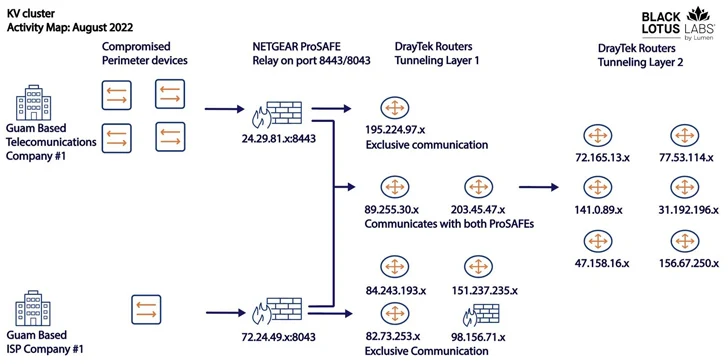
The two clusters – codenamed KV and JDY – are said to be distinct yet working in tandem to facilitate access to high-profile victims as well as establish covert infrastructure. Telemetry data suggests that the botnet is commandeered from IP addresses based in China.
While the bots part of JDY engages in broader scanning using less sophisticated techniques, the KY component, featuring largely outdated and end-of-life products, is assessed to be reserved for manual operations against high-profile targets selected by the former.
It’s suspected that Volt Typhoon is at least one user of the KV-botnet and it encompasses a subset of their operational infrastructure, which is evidenced by the noticeable decline in operations in June and early July 2023, coinciding with the public disclosure of the adversarial collective’s targeting of critical infrastructure in the U.S.
Microsoft, which first exposed the threat actor’s tactics, said it “tries to blend into normal network activity by routing traffic through compromised small office and home office (SOHO) network equipment, including routers, firewalls, and VPN hardware.”
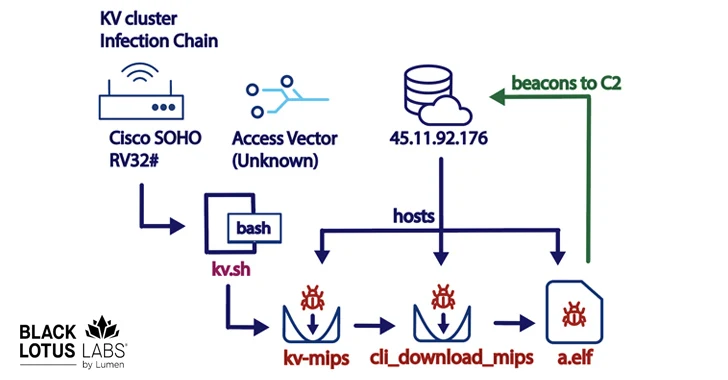
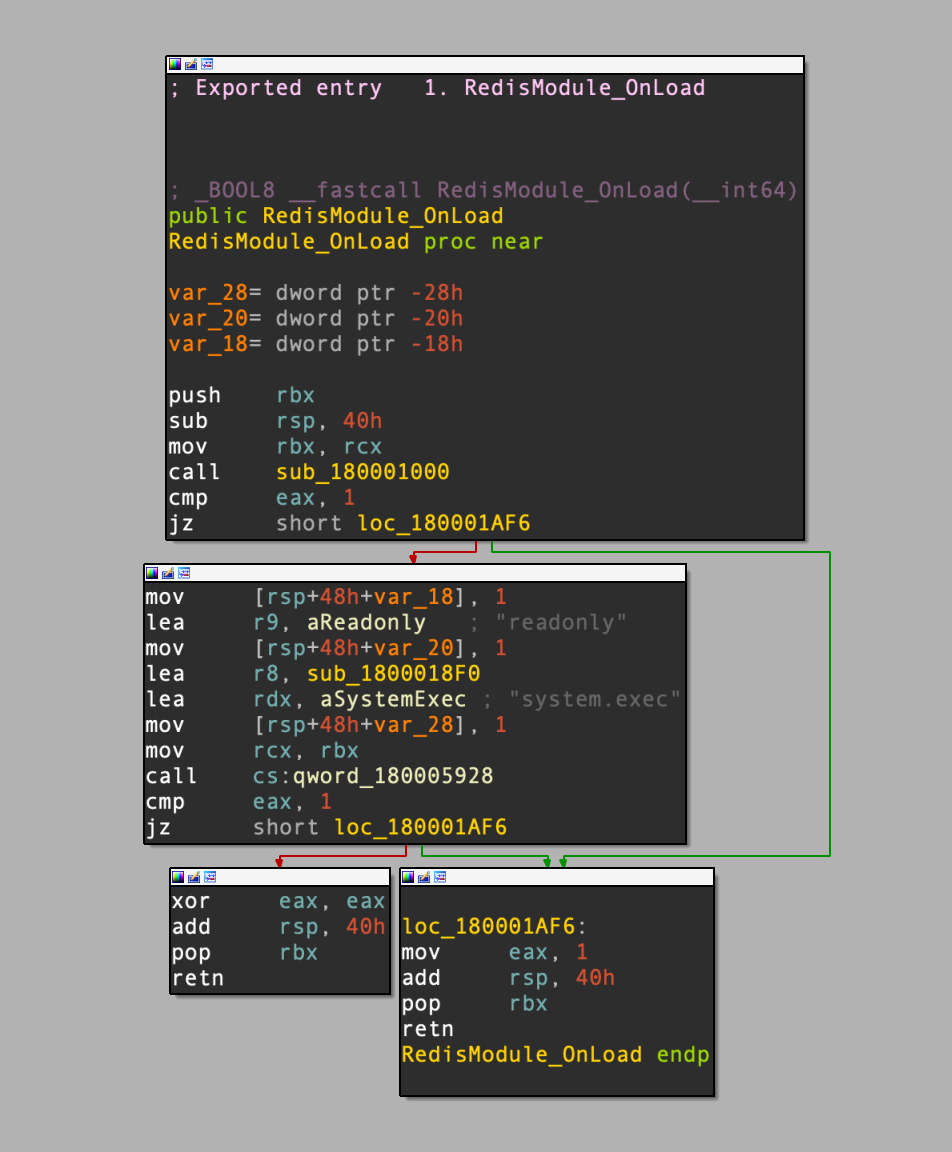
The exact initial infection mechanism process used to breach the devices is currently unknown. It’s followed by the first-stage malware…