IoT security realities – worse than you think
Juniper Research forecasts that IoT security spending will reach US$6 billion by 2023, with growing business risk and regulatory minimum standards that would serve as key spending drivers.
Commissioned by Armis, The Forrester report, State of Enterprise IoT Security in North America, revealed that 74% of the respondents felt their security controls and practices were inadequate for managed, unmanaged assets across IT, cloud, IoT devices, medical devices (IoMT), operational technology (OT), industrial control systems (ICS), and 5G.
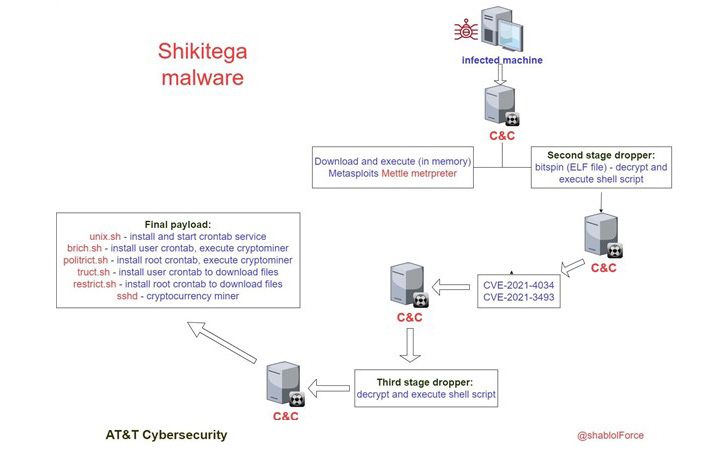
Keith Walsh, OT security and operations director at Armis, says the trouble with many installations within organisations is that each department tends to go solo on management and risk containment.
He cites the example of departments that may have managers over OT/ICS facilities, for instance: air conditioning, sanitation, telecommunications, and other functions. Server rooms and computers of all shapes and sizes may be managed by a separate IT department.
Outside a typical office, a process plant in the oil and gas, petrochemicals, and chemicals industries, or a power plant (nuclear, other renewable, or fossil), will yet have different field operations and maintenance managers managing various safety and other controllers. The expertise demanded by these fields tends to be disparate and so it would be difficult to converge all such manageable assets into a single department or system.

“For unmanaged devices, which may include OT and IoT, these may yet be another hurdle for organisations, since they may never have been defined as a security hazard, until recent times when 5G/LTE and broadband have permeated throughout every facet of an organisation.”
Keith Walsh
“So, it is safe to say, we can imagine the typical organisation may not have a complete security profile for all managed and unmanaged devices. Asset visibility is the first step in developing a security framework. You can’t secure what you can’t see,” he added.
As more devices in the homes connect to the internet, security and privacy concerns rise to new levels. The Palo Alto Networks’ The Connected Enterprise: IoT Security Report 2021…