Security audit raises severe warnings on Chinese smartphone models

The Lithuanian National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) recently published a security assessment of three recent-model Chinese-made smartphones—Huawei’s P40 5G, Xiaomi’s Mi 10T 5G, and OnePlus’ 8T 5G. Sufficiently determined US shoppers can find the P40 5G on Amazon and the Mi 10T 5G on Walmart.com—but we will not be providing direct links to those phones, given the results of the NCSC’s security audit.
The Xiaomi phone includes software modules specifically designed to leak data to Chinese authorities and to censor media related to topics the Chinese government considers sensitive. The Huawei phone replaces the standard Google Play application store with third-party substitutes the NCSC found to harbor sketchy, potentially malicious repackaging of common applications.
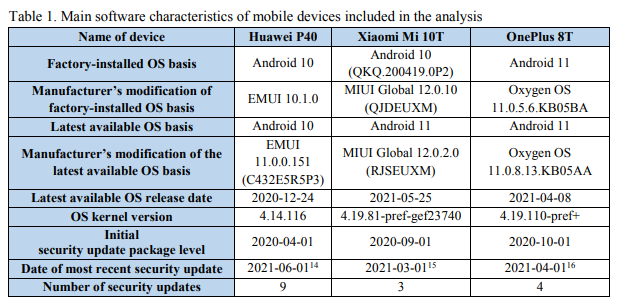
Huawei’s P40 is still stuck on Android 10, while Xiaomi ships with 10 but can be upgraded to 11. Only the OnePlus 8T shipped from the factory with Android 11 installed.
The OnePlus 8T 5G—arguably, the best-known and most widely marketed phone of the three—was the only one to escape the NCSC’s scrutiny without any red flags raised.
Xiaomi Mi 10T 5G
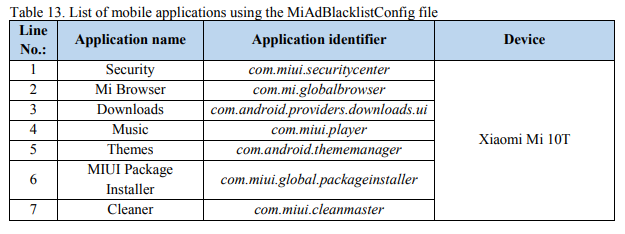
The NCSC found that seven default system apps on the Xiaomi phone can monitor media content for blocking from the user, using a regularly downloaded JSON file.
Xiaomi’s Mi 10T 5G ships with a nonstandard browser called “Mi Browser.” The NCSC found two components in Mi Browser which it didn’t like—Google Analytics, and a less familiar module called Sensor Data.
The Google Analytics module in Mi Browser can read from the device’s browsing and search history and can then send that data to Xiaomi servers for unspecified analysis and use. The Google Analytics module is activated automatically by default during the phone’s first activation or after any factory reset.
The NCSC found that Sensor Data’s module collects statistics on 61 parameters related to application…


