Norton Anti-Virus is Becoming a Crypto Mining Botnet
In the before-times – the heady days of 2017 when the prices of both Bitcoin and Ethereum skyrocketed and seemed immune to gravity – several well-known companies boosted their value by claiming to build new products on the blockchain or to create a solid trustworthy crypto-coin. The trend has continued through the pandemic.
We often note a whiff of desperation in old-economy businesses trying to re-invent themselves as blockchain or crypto companies. For example, according to Krebs On Security, RadioShack relaunched in 2020 as an online brand and “now says it plans to chart a future as a cryptocurrency exchange” by helping old-school customers feel comfortable with crypto speculation. We know that a few years ago photo giant Kodak, whose primary product was replaced by ubiquitous digital cameras on smartphones, announced moves into cryptocurrency called KodakCoin and Kodak KashMiner which quickly and temporarily boosted Kodak’s stock price 60%. The New York Times stated at the time, “Almost immediately, critics pounced on the company’s plans, characterizing them as a desperate money grab.” Kodak soon abandoned the coin and digital mining effort and Kodak now claims to be a drug company. Who is next, Blockbuster as NFT-factory?
No, the newest surprising news is Norton LifeLock as a crypto miner. Not that Norton LifeLock is an old-economy company, but it is a relatively stogy security firm offering a two-decade-old product that seems less relevant now than it used to be. In the internet age, software firms from the 1990s may count as “old-economy.”
Norton LifeLock has started offering the “Norton Crypto” tool as part of its famous yellow-branded Norton 360 software for home and business computers. Norton Crypto allows paying customers to mine cryptocurrencies while their computers are otherwise inactive. When the tool is turned on, Norton brings together all of its customers’ mining capacity into a pool of computing power that mines Ethereum then breaks the value of the mined currency into pieces and deposits a small percentage into a Norton…


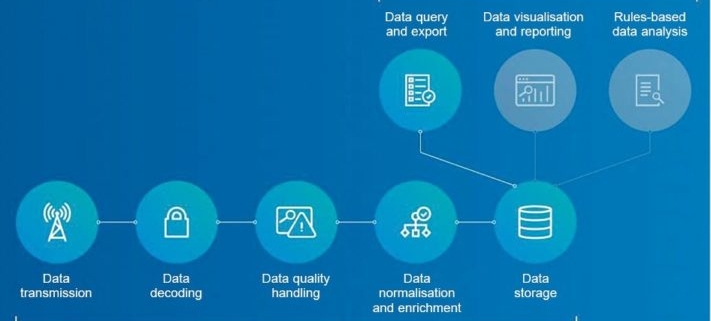
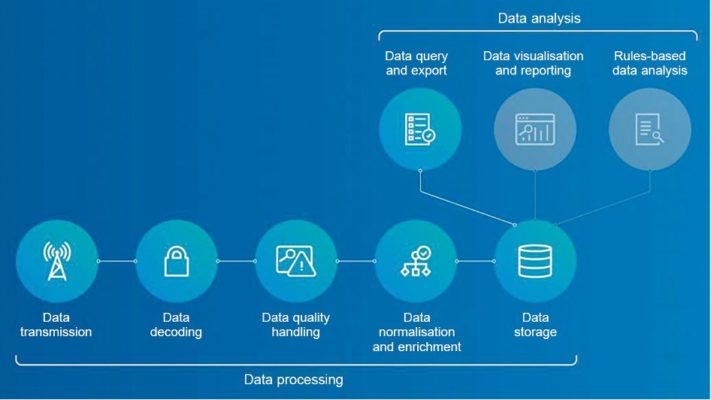
 Fig.2: Steps in IoT data management ( Source:
Fig.2: Steps in IoT data management ( Source: 