Top 5 Global Cyber Security Trends of 2023, According to Google Report
It is taking less time for organisations to detect attackers in their environment, a report by Mandiant Consulting, a part of Google Cloud, has found. This suggests that companies are strengthening their security posture.
The M-Trends 2024 report also highlighted that the top targeted industries of 2023 were financial services, business and professional services, tech, retail and hospitality, healthcare and government. This aligns with the fact that 52% of attackers were primarily motivated by financial gain, as these sectors often possess a wealth of sensitive — and therefore valuable — information.
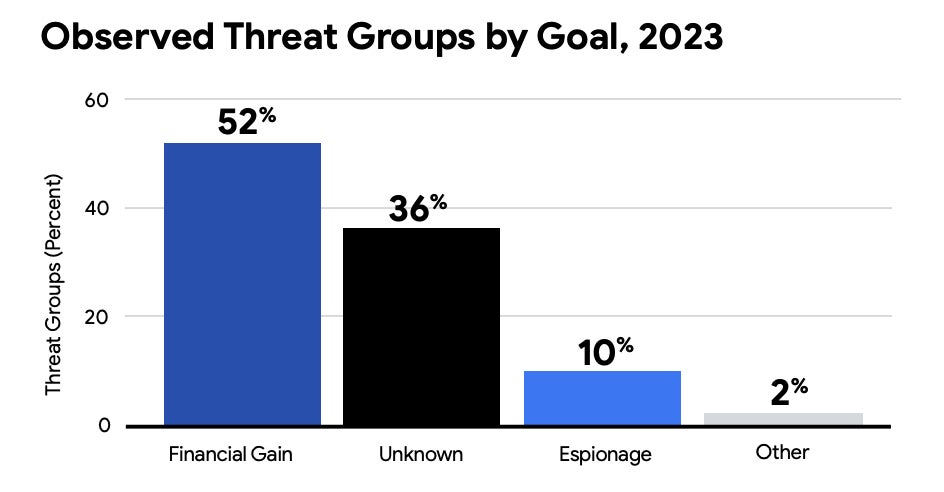
Financially-motivated activity was found to have gone up by 8% since 2022, which is partially explained by the parallel rise in ransomware and extortion cases. The most common ways that threat actors gained access to a target network were through exploits, phishing, prior compromise and stolen credentials.
Dr Jamie Collier, Mandiant Threat Intelligence Advisor Lead for Europe, told TechRepublic in an email: “Despite the focus on ransomware and extortion operations within the security community, these attacks remain effective across a range of sectors and regions. Extortion campaigns therefore remain highly profitable for cyber criminals.
“As a result, many financially-motivated groups conducting other forms of cyber crime have transitioned to extortion operations in the last five years.”
TechRepublic takes a deeper look into the top five cyber security trends of 2023 and expert recommendations highlighted by the 15th annual M-Trends report:
- Global organisations are improving their cyber defences.
- Cyber criminals have an increased focus on evasion.
- Cloud environments are being targeted more often.
- Cyber criminals are changing tactics to bypass MFA.
- Red teams are using AI and large language models.
1. Global organisations are improving their cyber defences
According to the M-Trends report, the median dwell time of global organisations decreased from 16 days in 2022 to 10 days in 2023 and is now at its lowest point in more than a decade. The dwell time is the amount of time…





