Attackers bypass Microsoft patch to deliver Formbook malware
Sophos Labs researchers have detected the use of a novel exploit able to bypass a patch for a critical vulnerability (CVE-2021-40444) affecting the Microsoft Office file format.
The attackers took a publicly available proof-of-concept Office exploit and weaponized it to deliver Formbook malware. The attackers then distributed it through spam emails for approximately 36 hours before it disappeared.
From CAB to “CAB-less” exploit to bypass the patch for CVE-2021-40444
The CVE-2021-40444 vulnerability is a critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability that attackers can exploit to execute any code or commands on a target machine without the owner’s knowledge. Microsoft released an urgent mitigation followed by a patch in September. A few days later, the company shared how attackers have been exploiting the flaw to deliver custom Cobalt Strike payloads.
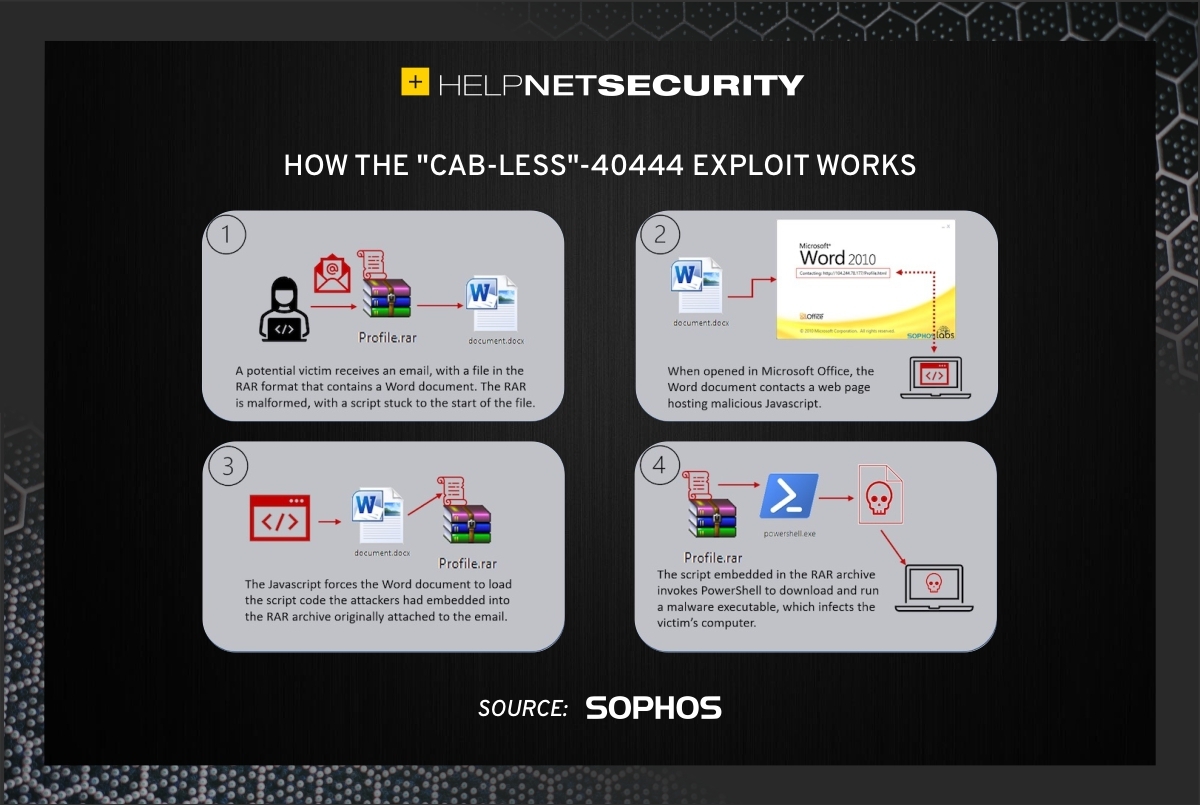
Sophos researchers found the 36 hours-campaign featuring the new exploit in late October. They discovered that attackers have reworked the original exploit by placing the malicious Word document inside a specially crafted RAR archive. The newer, “CAB-less” form of the exploit successfully evades the original patch.
Sophos data shows that the amended exploit was used in the wild for around 36 hours. According to the researchers, the limited lifespan of the updated attack could mean it was a “dry run” experiment that might return in future incidents.
“In theory, this attack approach shouldn’t have worked, but it did,” said Andrew Brandt, principal threat researcher at Sophos.
“The pre-patch versions of the attack involved malicious code packaged into a Microsoft Cabinet file. When Microsoft’s patch closed that loophole, attackers discovered a proof-of-concept that showed how you could bundle the malware into a different compressed file format, a RAR archive. RAR archives have been used before to distribute malicious code, but the process used here was unusually complicated. It likely succeeded only because the patch’s remit was very narrowly defined and because the WinRAR program that users need to open the RAR is very fault tolerant and doesn’t appear to mind if the archive is malformed, for…